When businesses are ready to scale, hiring the right people becomes one of the most critical factors for success. According to LinkedIn’s The Future of Recruiting 2023 report, 87% of recruiters say hiring has become more strategic than ever before. That’s why measuring the right hiring metrics has become a business necessity.
So what exactly should companies be tracking? And how do these numbers translate into smarter decisions and stronger teams? In this article, we’ll dive into the 5 most important hiring metrics, explain why they matter, and show companies how to track them.
What Are Hiring Metrics?
Hiring metrics, sometimes referred to as recruitment metrics or talent acquisition metrics, are a set of data-driven indicators used by organizations to assess, manage, and refine their hiring efforts. These measurements provide visibility into what’s working (and what’s not) within the recruitment pipeline, empowering teams to make smarter, more strategic decisions.

Beyond efficiency and performance, hiring metrics can also be tied to broader organizational goals such as diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI). By tracking representation across various stages of the recruitment process, businesses can identify bias, ensure fairness, and work toward a more inclusive workplace.
It’s also important to distinguish between two often-overlapping but distinct areas: recruitment and talent acquisition. While both aim to fill roles, their objectives and scope differ, and so do the metrics that track for each:
- Recruiting metrics track short-term, tactical outcomes like time-to-fill or cost-per-hire.
- Talent acquisition metrics, on the other hand, focus on long-term hiring strategy and pipeline health.

Recruiting metrics vs. Talent acquisition metrics
Today, with 98% of Fortune 500 companies using applicant tracking systems (ATS) to sort and manage resumes, businesses have access to a wealth of recruitment data. When used strategically, this data allows hiring teams to assess the success of their recruiting strategies, identify gaps, and make smarter decisions that lead to better hires.
Why Should Businesses Track Their Hiring Metrics?

Why businesses track hiring metrics
Minimize bias with data-driven hiring
Relying on gut feelings or first impressions in hiring introduces subjective bias, often unconsciously. This can lead to poor hiring decisions based on affinity bias (favoring people similar to ourselves) or confirmation bias (favoring those who reinforce existing beliefs). Hiring metrics offer a more objective and structured way to evaluate candidates.
For example, using data like skills assessment scores helps ensure that candidates are selected based on their ability to perform the job, not personal impressions. This approach not only improves the overall quality of hire but also strengthens DEI by creating a more level playing field for all applicants.
Identify and prioritize the best recruitment sources
Recruiters often use a mix of job boards, social platforms, employee referrals, and recruitment agencies to source candidates. But not all channels perform equally. Tracking hiring metrics allows businesses to identify which sources consistently bring in high–quality applicants and which ones fall short.
With this insight, companies can allocate their recruiting budget more effectively, focus on high-performing channels, and eliminate those that underdeliver – ultimately saving time and reducing unnecessary spending.
Fuel business growth with smarter strategies
Strategic hiring fuels long-term business success. By tracking key metrics like time to hire, cost per hire, offer acceptance rate, and retention, companies gain a clearer picture of the effectiveness and impact of their recruitment process.
This data empowers HR leaders to make informed decisions, such as investing in more efficient hiring tools, improving candidate screening procedures, or enhancing employer branding in recruitment to attract top-tier talent. In the bigger picture, hiring metrics align recruitment efforts with broader business goals and guarantee that workforce planning supports growth.
5 Critical Hiring Metrics To Track

5 critical hiring metrics
Time to hire
Time to hire is the number of days between when a candidate first enters the pipeline, either by applying or being sourced, and the moment they accept the job offer. This metric reflects the efficiency of the recruitment process and plays a major role in candidate experience. A long time to hire can signal internal delays in communication, screening, interviews, or decision-making. These delays not only increase the risk of losing top talent but may also negatively impact your employer brand.
How to measure time to hire: Record the date the successful candidates applied for the role and the date they accepted the offer. Subtract the first date from the second to get the total number of days.
Cost per hire
Cost per hire measures the total amount organizations spend to fill an open position. It includes both internal and external expenses such as: job advertising, recruitment software, career events, agency fees, background checks, and interview-related travel costs. Monitoring this metric helps organizations understand the financial efficiency of their hiring strategies and make informed budget decisions. It’s also useful for comparing the ROI of different sourcing channels.
How to measure cost per hire: Add up all recruiting-related expenses within a given period, then divide that total by the number of hires made during that same timeframe. For example, if you spent $50,000 to hire 10 people in a quarter, your cost per hire would be $5,000.
Offer acceptance rate
Offer acceptance rate reflects how often candidates say “yes” to the job offers. This metric provides insight into how attractive the offers are and how well the recruitment process aligns with candidate expectations. A low acceptance rate may indicate issues with compensation, job role clarity, or candidate experience. On the other hand, a high acceptance rate suggests that the hiring team is effectively engaging the right candidates and presenting competitive offers.
How to measure offer acceptance rate: Divide the number of accepted offers by the total number of offers extended. Multiply the result by 100 to get the acceptance percentage.
DEI metrics
Tracking metrics related to DEI can help organizations identify opportunities to improve their hiring process and create a more diverse and inclusive workforce. Attracting candidates from underrepresented groups is a good start, but tracking how they move through your recruitment funnel is essential. For example, a significant drop-off of minority candidates at the interview stage may indicate biases in the selection process.
How to measure DEI metrics: Keep track of the diversity of the applicant pool and how many candidates from different minority groups make it to each stage of the recruitment process. Compare these numbers to overall hiring rates to identify potential disparities or improvement areas.
Quality of hire
Quality of hire measures the long-term success and impact of new hires within the organization. It evaluates whether a new employee performs well, fits the company culture, and contributes to business outcomes. This metric goes beyond short-term efficiency and focuses on whether the hire was the right decision in the long run. It’s especially useful in understanding the effectiveness of your sourcing, screening, and interviewing strategies.
How to measure quality of hire
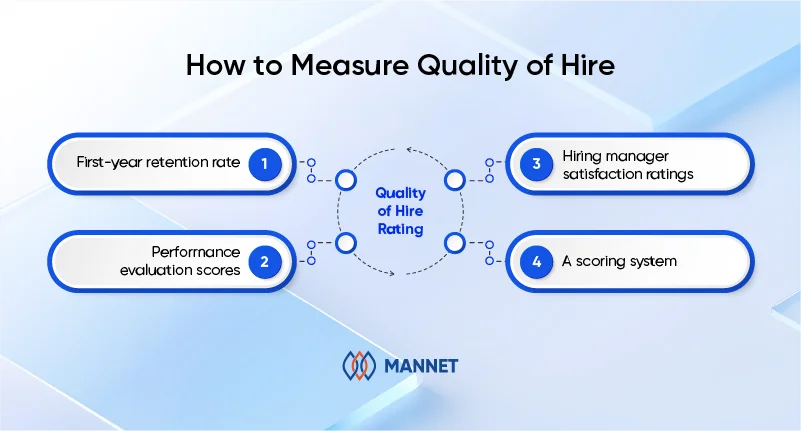
How to measure quality of hire: Use a combination of metrics such as first-year retention rate, performance evaluation scores, and hiring manager satisfaction ratings. Many companies use a scoring system to rate each factor (e.g., on a scale of 1–5), then average those scores to create an overall quality of hire rating.
FAQs About Hiring Metrics
- What are hiring metrics?
Hiring metrics are quantifiable data points that assess the efficiency, effectiveness, and quality of your recruitment process. They help organizations make informed decisions by highlighting areas of success and identifying opportunities for improvement in hiring strategies.
- How can I track hiring metrics effectively?
To track hiring metrics effectively, organizations should use recruitment tools such as ATS or Human Resource Information Systems (HRIS). These platforms can automatically collect and analyze data across different stages of the hiring process. It’s also helpful to set clear goals for each metric, define consistent tracking methods, and ensure collaboration between recruitment and HR teams to interpret the data meaningfully.
- How often should hiring metrics be reviewed?
Companies should review hiring metrics regularly – typically on a monthly or quarterly basis. The review frequency may depend on your hiring volume and business needs. Frequent reviews allow recruitment teams to identify trends, address bottlenecks, and make timely improvements to the hiring process. It also ensures that your strategies stay aligned with evolving business objectives and labor market conditions.
A Summary of Hiring Metrics
In conclusion, hiring metrics are essential for evaluating the effectiveness and efficiency of your hiring process. By tracking key indicators like time-to-hire, cost-per-hire, and quality-of-hire, companies gain the insights needed to refine their recruitment strategy and continuously improve.
But tracking numbers alone isn’t enough. You need the right expertise to interpret them and act on what they show. That’s where ManNet can support you, not just with data but with real solutions to improve hiring outcomes. From sourcing to onboarding, we provide recruiting services that help you build teams that fit, stay, and perform.
Let’s contact us if you’re ready to hire with more insight and less guesswork.




